
Understanding Body Composition and Nutrition
Explore the science of how your body works
Body Composition Explained
What is Body Composition?
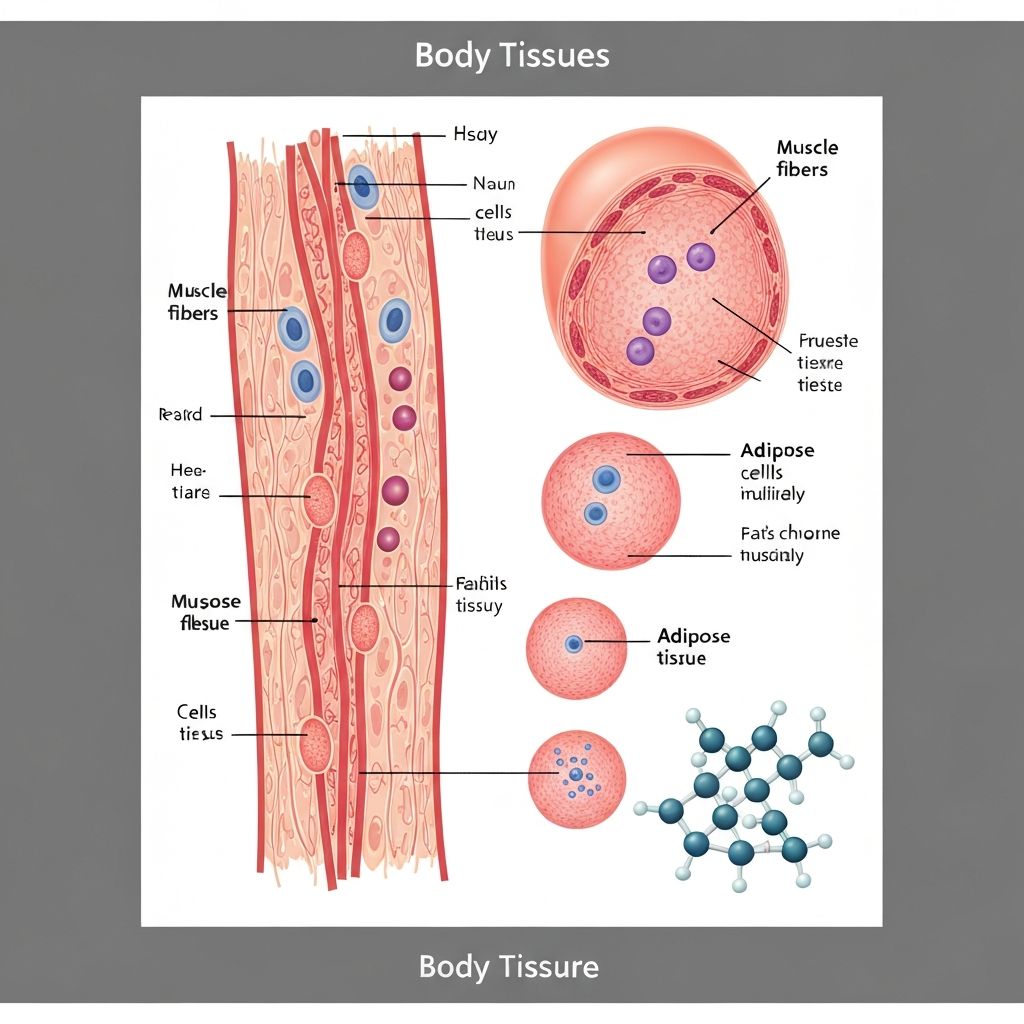
Body composition refers to the breakdown of your body into different tissue types. Your body consists of muscle tissue, adipose tissue (fat), bone, water, and organs. Understanding these components helps explain how bodies function and how energy is utilized in everyday activities.
The distribution and proportion of these tissues vary among individuals based on genetics, activity levels, nutrition, and age. All body types and compositions are valid; the science of body composition is purely descriptive, not prescriptive.
Common Misunderstandings About Body Weight
Beyond the Scale
Weight alone does not indicate body composition. Two people of the same height and weight can have entirely different compositions. Muscle tissue is denser than fat tissue, so changes in body composition may not always reflect changes on a scale.
The human body is complex. Weight fluctuates daily due to hydration levels, food intake timing, hormonal cycles, and sodium consumption. A single number cannot accurately represent health or wellness.
Rather than focusing on weight, understanding the roles of different tissues and how nutrition and activity affect them provides more meaningful insights into how bodies function.
The Role of Nutrients in Tissue Maintenance

Macronutrients and Function
Proteins are essential building blocks. They support muscle tissue maintenance, immune function, enzyme production, and hormone synthesis. Amino acids from protein sources are used throughout your body for various physiological processes.
Carbohydrates provide energy for brain function and physical activity. They are stored as glycogen in muscles and liver for use during activity and rest periods.
Fats play crucial roles in hormone production, nutrient absorption, brain function, and cell structure. Fatty acids are essential components of cell membranes and support numerous metabolic processes.
A variety of whole food sources—vegetables, fruits, whole grains, legumes, nuts, seeds, fish, and eggs—provides the diverse nutrient profiles your body requires.
Influence of Rest and Activity on Energy
Energy Expenditure Throughout the Day
Your body expends energy at rest (basal metabolic rate), during daily activities, and during intentional exercise. All movement—from walking to working—contributes to overall daily energy expenditure.
Rest and recovery are equally important as activity. During sleep and relaxation, your body performs critical maintenance functions: muscle protein synthesis, hormone regulation, cognitive consolidation, and immune function.
Hydration supports these processes. Water is essential for nutrient transport, temperature regulation, joint lubrication, and cellular function. Adequate intake varies based on activity level, climate, and individual factors.
The relationship between activity, rest, nutrition, and hydration creates the foundation for how your body functions day to day.

Explore More
What Body Composition Really Means
A deeper look at tissue types, their functions, and what composition science actually tells us about how bodies work.
Continue to full article →
Nutrients and Their Basic Functions
Explore the roles of proteins, carbohydrates, and fats in supporting your body's daily functions and maintenance.
Continue to full article →
Everyday Influences on Metabolic Processes
Understanding how activity, nutrition, sleep, and hydration affect your body's energy systems and metabolism.
Continue to full article →Frequently Asked Questions
Weight is a single measurement of total body mass. Body composition describes the breakdown of that mass into different tissue types: muscle, fat, bone, water, and organs. Two people of identical weight and height can have very different body compositions because muscle is denser than fat tissue.
Hydration is essential for every cellular process. Water supports nutrient transport, temperature regulation, joint function, and metabolic processes. Daily fluid needs vary based on activity level, climate, and individual factors. Adequate hydration supports tissue maintenance and overall physiological function.
Proteins are made of amino acids that serve as building blocks for muscle tissue, enzymes, hormones, and immune system components. Protein supports tissue maintenance and repair, plays roles in hormone regulation and immune function, and contributes to satiety. Diverse protein sources include legumes, nuts, fish, eggs, dairy, and grains.
Physical activity influences energy expenditure and can affect tissue composition over time. Different types of activity—strength training, cardiovascular exercise, daily movement—have different effects on body systems. Combined with adequate nutrition and rest, regular activity plays a role in tissue maintenance and metabolic function.
Carbohydrates are a primary energy source for your brain and body. They include simple sugars and complex carbohydrates (starches and fiber). Whole food carbohydrate sources—vegetables, fruits, whole grains, legumes—provide energy, fiber for digestive health, and various micronutrients.
Dietary fat is essential for hormone production, nutrient absorption (especially fat-soluble vitamins A, D, E, K), brain function, and cell structure. Different fatty acids have different roles. Sources include nuts, seeds, fatty fish, oils, and whole foods. Fat is calorie-dense but plays vital roles in physiological function.
Sleep is essential for tissue maintenance and metabolic regulation. During sleep, your body performs muscle protein synthesis, releases growth hormone, regulates metabolic hormones like cortisol and insulin, and consolidates cognitive memory. Adequate sleep supports proper metabolic function and tissue maintenance.
Body composition is highly individual and influenced by genetics, age, sex, activity history, and nutrition. There is no single "ideal" composition—all bodies are different and valid. The science of body composition is descriptive, helping us understand how tissues function, not prescriptive about how bodies should look.
Explore Our Blog for More Information
Discover detailed articles on body composition science, nutrition fundamentals, and how everyday factors affect your health.
View All ArticlesEducational content only. No medical services. No promises of outcomes.
This website provides informational content about body composition and nutrition fundamentals. It is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Individual circumstances vary widely, and what applies to one person may not apply to another. For personalized guidance related to health conditions or concerns, please consult with a qualified healthcare professional.